Understanding Futures Trading: A Beginner’s Guide to Using Derivatives for Hedging and Speculation

Futures trading has become an essential tool for investors looking to hedge risks or speculate on the price movements of various assets. But what exactly are futures contracts, and how can they be used effectively?
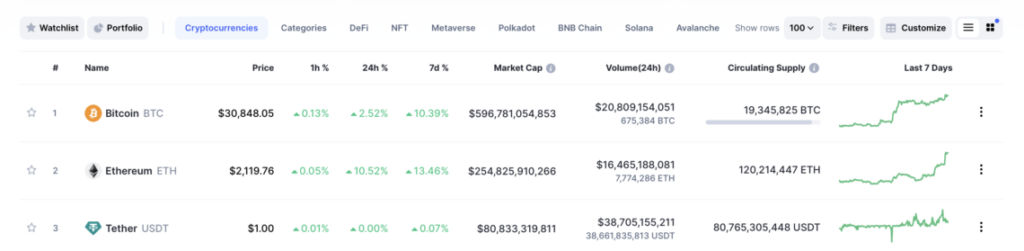
A futures contract is a standardized legal agreement to buy or sell a particular asset at a predetermined price at a specified time in the future. These contracts are traded on regulated exchanges and commonly involve commodities like oil and wheat, financial instruments such as currencies and interest rates, or indices like the S&P 500.
There are two primary reasons investors use futures:
Hedging: Businesses and investors use futures to protect themselves against price fluctuations. For example, a wheat farmer may sell futures contracts to lock in a price for his crops months before harvest. If the market price drops later, the futures contract ensures he still receives the agreed amount.
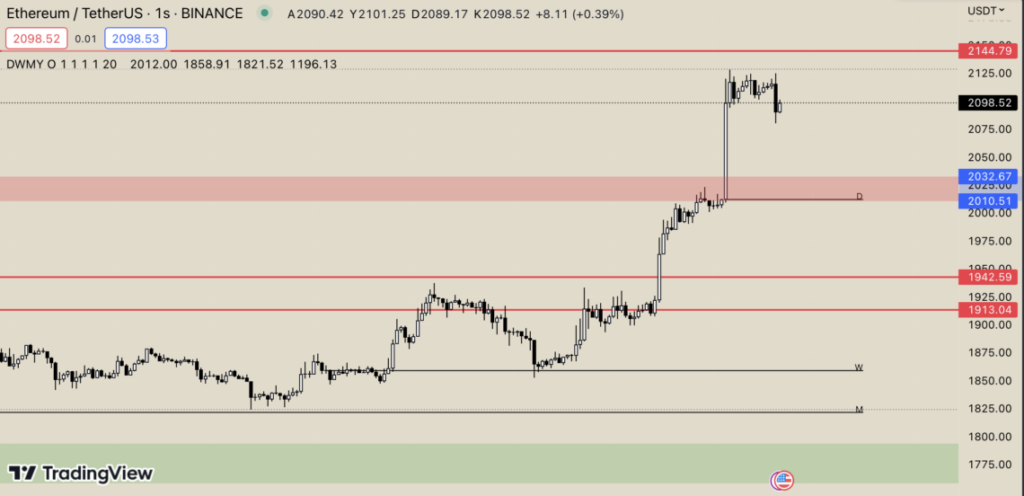
Speculation: Traders often use futures to profit from expected price changes. By taking long (buy) or short (sell) positions, they aim to benefit from market movements. However, this strategy involves high risk and requires deep market understanding and discipline.
Futures trading offers leverage, meaning traders can control large positions with relatively small capital. While this magnifies potential profits, it also increases the risk of substantial losses.
Understanding margin requirements, contract expiration dates, and market volatility is crucial before entering the futures market. Beginners are advised to start with educational resources or simulated trading platforms before risking real capital.
Futures are powerful financial instruments, but like any tool, they must be used wisely. Proper risk management and a well-thought-out strategy are key to success in the world of derivatives.


 English
English